
Universidade de Lisboa
Faculdade de Psicologia e
de Ciências de Educação
Coordinators
Ana Margarida Veiga Simão
Belmiro
Cabrito
Elisabete
Rodrigues

Socrates- programme
Comenius 2.1
June 2004
Students:
Cátia Costa
Joana Carvalho
Marcelo Correia
Luís Rosário
Testing of materials in institution
1.
The
institution
Presentation
It is a primary school, built
in early 1950ies, in the centre of Lisbon.
The curriculum and
educational project obey to the Official Plan launched by the Ministry of
Education and their main aims are to offer a common teaching that promotes the
development of the memories, critical thinking, esthetical mind, moral sense and
solidarity values.
Human Resources
In the school work 18
basic teachers, 1 preschool teacher, 2 teacher trainees, 2 cultural animators,
4 educational aid professionals and a security guard. Besides the regular
classes, children take acquaintance with music, gymnastic and swimming. The
school gets in a pedagogical garden and theatre courses.
Childrens parents have
created a Parents Association in order to help the teachers to work with
children in non-curricular activities (ATL - free time activities).
Material Resources
The building has 2
floors with 4 classrooms each and sanitary room. In the first floor is placed
the teachers room.
Among the 8 rooms, 6 of
them serve only to teaching activities. The other two functions as the gym and
the library.
The students
The school has 193
students, in all the 4 classes of the primary cycle with 6 to 12 years old.
Most students come from
the neighbourhood and they belong to the medium and lower medium social
classes. Poor students are around 30% of the total number.
Free time activities
88% of the pupils go to
ATL. They do swimming and computing.
Projects
The school develops some
projects such as Castles in the air, Internet at the school; Theatre,
Pedagogical garden, Play Gym and Foreign languages English and other
activities with external partners, such as the Town Hall, the local church, the
Health Centre and the Teacher Training Centre.
The Educational Project
All the activities are supported on the
intention Learning with the past, educating in the present, building the
future.
2. The classes
The experiences occurred in two classrooms, A
and B.
The students of the A
room
|
Nº of
students
|
Genre
|
Age
|
Preschool
experience
|
Social
Class
|
|
19
|
Female:
10
Male: 9
|
7 years
old (all students)
|
18
|
Higher
4
Medium
11
Low
medium 3
Low - 1
|
The students of the B
room
|
Nº of
students
|
Genre
|
Age
|
Preschool
experience
|
Social
Class
|
|
18
|
Female:
10
Male: 8
|
6 years
old (all students)
|
16
|
Higher
Medium
Low
medium
Low
|
3. Tested material
The Cassette
Recorder
Activities:
- Hear, produce and feel tones /
noises.
- Sound can be bundled.
- Tones / sound is a wave. Sound
can be made visible, sound can make items move.
- Examination of a loudspeaker:
How does it look and what does it consist of?
- Examination of the way a
cassette recorder functions.
Teaching Plan
Project: ETE
Institution: School nº 151
Theme: Cassette Recorder
Aims:
-
To
sensitise female to work in technological areas
-
To
promote curiosity and the taste for technology
-
To
recognise the importance of technological teaching in early years
-
To
develop critical thinking in educators and students
4. Evaluation/results
tools used to get results
FROM CHILDREN
Activity 1-Hear,
produce and feel tones / noises

Materials
With a cross, answer to
the following questions:
What did you like the most?
To play animals
To follow the sound with
the eyes closed
To built a sound
instrument
To feel vocal ropes
Everything
What didnt you like?
Anything
Everything
To play animals
To follow the sound with
the eyes closed
To built a sound
instrument
To feel vocal ropes
Everything
Evaluate your knowledge. Signalize with a cross the wrong answers
Vocal ropes vibrate more
when we speak higher
The instrument we have
built is a rope instrument
The sound is always the
same, independently the boxes used
The rubbers vibrate
better in the empty box

The children build an instrument

Some instruments built
Activity 2 - Sound can be
bundled

Materials
Answer to the
following questions:
1. What did you like
the most? __________________________________________
2. What didnt you
like?_______________________________________________
Evaluate your knowledge
- What happen when we talk to the
tube? ________________________________
- To where does the sound move in
the telephone? _________________________

Making a telephone
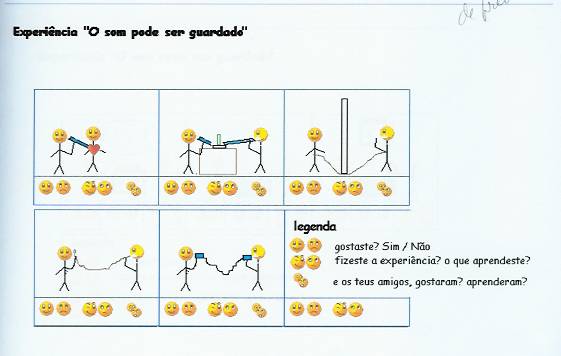
Sound can be bundled
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meaning
Did you like? Yes/No
Did you make the experience? What did you learned?
And what about your friends, did they like? What did they learn?
|
|
|
|
|

Activity 3 - Tones / sound is a wave. Sound can be made visible, sound
can make items move.

Materials
Draw in
each empty space:
|
What you
did like
|
What you
didnt like
|
|
|
|
Activity 4 - Examination of a loudspeaker: How does it look and what
does it consist of?

Materials
|
What did
you like most?
|
What
didnt you like?
|
|
|
|
|

Activity 5 -
Examination of the way a cassette recorder functions

Materials
Paying attention to this last activity, it has
been decided to get the feedback in audio.
The questions done concern not only the
teaching of this activity but also the examination of a loudspeaker, because
both instruments are very related one each other.


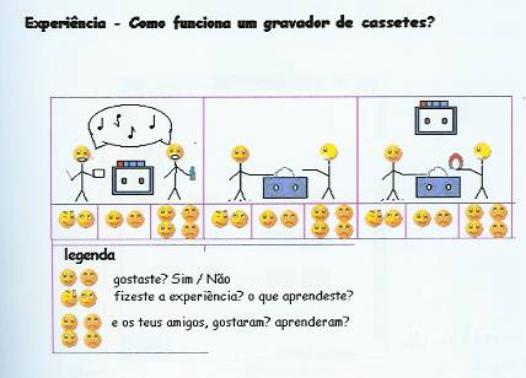
The way a cassette
recorder functions
|
|
Meaning
Did you like? Yes/No
Did you make the experience? What did you learned?
And what about your friends, did they like? What did they learned?
|
|

The questions done are:
- Whats
your name?
- How
old are you?
- What
is the interest of the button with a square drawn?
- How
did you call the objects that catch the clips?
- What
is the interest of the button with a circle drawn?
- From
all the activities what you have like the most?
- Which
object you have learned more with?
- The
loudspeaker connection cable is made of what?
- What
material is caught by the magnets?
- What
is the interest of the button with a triangle drawn?
- When
you play with the pencil and the magnet did they catch one each another?
Why?
- How
do you call the black parts of the loudspeaker?
- What
object have we taken to pieces?
tools used to get results
FROM Teachers
Interview guidelines FOR THE teacher
Theme: Early Technical Education
Objectives:
-
To
know teacher opinions about the project
-
To
think about the project
|
Block
|
Specific
Objectives
|
Questions
|
|
A
|
To evaluate the experiences in ETE
To characterize educational practice
To enumerate pedagogical aspects of the
activities
|
Do you think that the instructions are clear,
paying attention to the materials, the phases, etc?
How do you evaluate the interaction between
the group elements?
In what way you think that these experiences
answer to children needs?
Do you think that this project contributes to
the development of children social, technical and scientific skills?
|
|
B
|
To think over the children role in the
activities
|
Can you describe children reactions to
experiences, taking account the gender, in manipulation skills, curiosity,
autonomy and other skills?
How do you interpret the interaction between
the pupils one another?
How do you evaluate children adhesion to the
activities?
Do you notice gender differences in the
participation? Which ones?
What do you think that your pupils had
learned, considering the knowledge and its application, as well as the
individual development?
|
|
C
|
To indicate changes needed
To signalise the strong point and the weak points
of the activities
|
How do you evaluate the project?
What are the qualities and the problems of
the project?
What do you suggest to the project
development?
|
5. results
5.1
About the teacher and the teaching
A-
How the activity had occurred
The instructions are
good enough to get success in the experiences. The different phases proposed
are well synchronised. The choice of the materials reveals a good one, once the
materials are not very expensive and some of them can be got from used objects
(It was relatively easy to follow the instructions).
B Interaction
There has been a strong
interaction between the teacher, the students and the children. They have
helped one another. The pupils paid attention to the explanation and have
participate very much.
Among the pupils, they
have interacted well and strongly one with the others, in the manipulation of
the materials and objects.
But, the group must be
shorter, in order to get a more fruitful interaction and learning (the
learning is directly tied to the dimension of the group)
C Pedagogical
aspects
The experiments answer
to the curiosity of the children and their need to manipulate objects and to
make acquaintance with objects.
These experiences are
adequate to the children. They can manipulate objects, experiment with the
others, collaborate, etc. (I think that these activities are adequate. They
catch easily all the concepts).
C
Competencies
They developed technical
and social competences. They worked with experiences and materials that they have
never experimented. They try the flexibility of different materials. They have
done things in a way that they have never done. The practice was very useful to
the understanding of the technical situations and the concepts that, in this
way, are put in practical work.
They have registered
what they have done and seen, in draws and in a few statements. This demand was
very useful. They have thought about the experiences, in their way, and learnt
another time.
They have developed
social competences, namely team work and cooperative skills.
They developed
organisation skills, needed to express their feelings about they have done and
learned.
5.2
About children and learning
A How do
children react to the activity?
They like it very much.
They are very curious. They want to know all the names and how to do. They
react very well to the material.
They have put several
questions in order to understand concepts and to understand the meaning and
utility of some materials. They have been very interested (Yes, they do work
with me and have made questions
Besides, they brought materials from their
homes).
They have worked some
how autonomously and there have been no such a difference between boys and
girls. Inclusively, there were 3 girls more interested than the boys, in spite
of the boys in general seemed more interested. There were not visible gender
differences. (Gender differences, maybe not
Perhaps the boys group has been
more interested
It is an individual attitude ... both boys and girls are very
interested).
B How do
children react on another?
They worked already as a
group, once they have been last year in the same classroom. They collaborate
very much. (This year they are more
connected one to the other). Nevertheless, it seems that boys worked more with
boys and girls with girls (the group of the boys
the group of the girls).
C How do
children adhere to the activity?
The children,
independently their gender were very motivated for the activities. They were
very curious and collaborative. They questioned several times the teacher and
the students who did the experiences. They brought materials from their homes.
They were always very anxious regarding the days when ETE is going to happen.
D What do
children learn?
(Contributions to
)
They have learned some
technical concepts, which they had tried in experience.
They have learned the
importance of being rigorous.
They have learned about
the need of doing thinks.
They have learned how to
organise their work and their answers and questions.
They have learned
(developed) team work.
They have learned
cooperative attitudes.
No important differences
were noticed between boys and girls.
5.3 Suggestions from the
teacher and the students
The project is very
interesting but it must be enlarged in the experiments and concepts.
The work must be done
with small groups.
It will be important to
have a written manual and not only an on-line one.
The manual must have the
materials, the instructions, the objectives for each experience and some work
guidelines.
The experiences must pay
attention to some differences between each country, namely concerning the
teachers scientific and pedagogical basis.
It is important to train
teachers that are going to make ETE.
ETE must be a part of
teacher training.











